The Israeli security company JSOF recently discovered 19 vulnerabilities in the code of a TCP/IP implementation designed in the 90s that has been widely used across all major device types over the last 20 years. Hundreds of millions of devices from over 500 manufacturers are apparently at risk: from medical devices to printers to industrial control modules. The Israeli researchers have given the collection of gaps the name Ripple20.
Several of the vulnerabilities, if exploited, allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on target devices and to take over control of the devices: industrial control devices or medical devices, for example. In addition, Ripple20 could hide harmful code in devices for years. The ICS-CERT responsible for industrial controls rates the incident with a maximum severity of 10 on the CVSSv3 scale.
JSOF published the detailed report with CVE numbers and descriptions on its website.
Just apply a patch, right?
The problems were detected when JSOF analyzed a device and discovered that the TCP / IP stack contained vulnerabilities. The zero-day vulnerabilities were found in the widely used Treck embedded IP stack.
"Not that many people have heard of this company, but they are a leading provider of TCP-IP stacks, so they’re at the beginning of a really complex supply chain," said JSOF CEO Shlomi Oberman. The Israeli researchers called the gaps ‚Ripple‘ because they crawled up the supply chain and reached the big vendors from a relatively small provider. Treck's solutions are used by large manufacturers such as HP, Intel, Schneider Electric, Caterpillar and Rockwell Automation.
According to JSOF, the dangerous factor is that most devices using this library will remain unpatched, not only because the problem affects older devices that are difficult to patch, but mainly due to complex or untracked software supply chains. Many companies do not notice that they're using this vulnerable library as it doesn't appear in their code manifests.
Treck has fixed the gaps in version 6.0.1.67. How that should influence the affected devices remains largely open. According to CERT/CC, manufacturers should contact Treck itself. 'Customers who use a vulnerable device should contact their seller,' it says succinctly in the security notice of the CERT/CC, which coordinated the disclosure process. But how do customers find out if they have a problem? All those involved are currently silent about this. So far, there has apparently been no concrete test for vulnerability.
How does emnify secure my IoT solution?
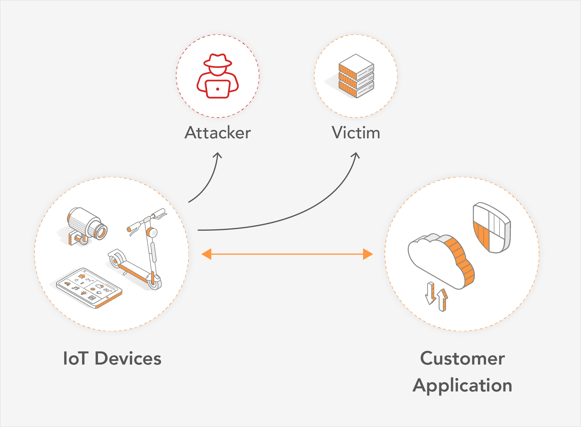
As mentioned in the JSOF publication, the vulnerabilities take advantage of unsecured remote access of IoT devices. emnify provides advanced and secured IoT device remote access solutions to guard against such vulnerabilities.
While there are a number of ways hackers target IoT devices, there is a lot you can do to monitor and optimize your IoT solution to build barriers against such attacks. For example, consider carefully your choice of connectivity options - Cellular, LoRa and WiFi perform differently in terms of IoT security.
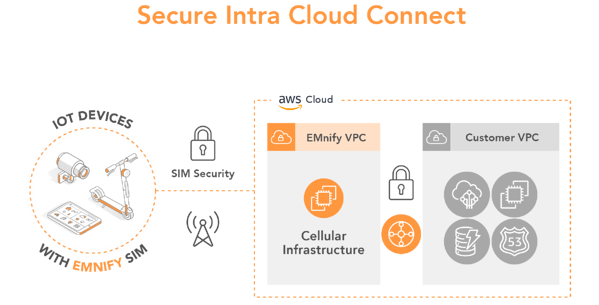
Traditional operators secure device data within mobile network using a SIM card but there is a security gap between the mobile network and the cloud; that’s were the data passes the public internet and your solution becomes vulnerable to attacks. emnify’s cellular cloud connectivity secures your solution with private static IP addresses that enable simple remote access via one virtual private network across all customer locations. The devices are not visible from the Internet and can be accessed by a VPN connection to the mobile network operator gateway.
For example, for customers using AWS, below is what your secured IoT solution looks like with emnify.
What else can I do to mitigate risk?
Another way to prevent attempts to steal remote access to IoT devices, as well as completely block attacks, is to use a cellular firewall. With a cellular firewall, devices are only permitted to communicate with a defined subset of IP addresses. The firewall itself is not located on the individual devices, rather on the cellular connection – out of the attacker’s control.
If you want to find out which other cellular features can be used to secure your IoT solution you can download our free Security Whitepaper below. The whitepaper has 25+ features and best practices that every enterprise can adopt to be safe from IoT attacks.
Get in touch with our IoT experts
Discover how emnify can help you grow your business and talk to one of our IoT consultants today!

emnify
The content team of emnify is specialized in all things IoT. Feel free to reach out to us if you have any question.